Meditation and the Polyvagal Theory
Applying the Polyvagal Theory in Your Meditation Practice
Defining the Three Responses
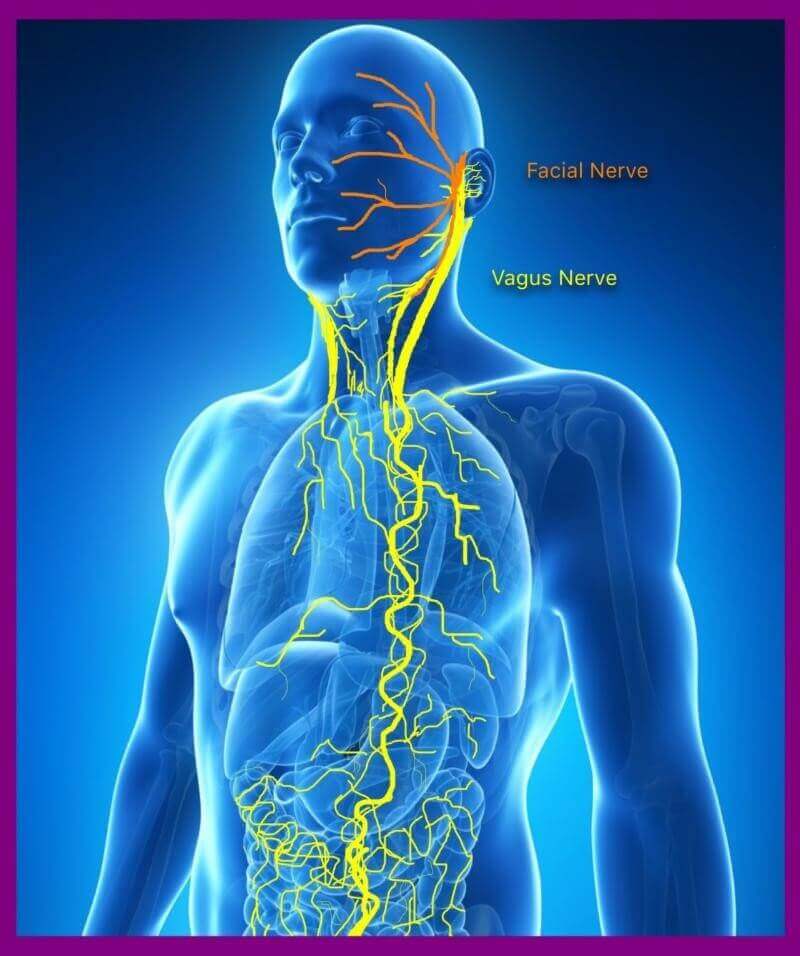
Activating the Vagus Nerve
Relax your Face Muscles
This is a meditation "trick" that many people do not know about. As written about in Chad Foreman's article on how a simple smile can relax your entire body . Because of the close connection between facial nerves and the vagus nerve simply by relaxing your face muscles you can instantly achieve a state of rest.
Deep Breathing
Aside from feelings of safety, another thing that can stimulate the vagus nerve is calm your system with some deep breathing exercises known as breathwork. Breathwork is hugely popular at the moment and polyvagal theory explains why it eliminates stress and activates deep states of relaxation so effectively. I highly recommend The Way of Meditation's course The Art of Breathing .
Chanting Om or Humming
Chanting Om has been shown to activate the vagus nerve too. You can simply hum or chant om, either works well. Chanting Om with a group is an incredible experience as the sound resonates through-out the whole room and it's easier to fully surrender and connect with the practice. The polyvagal theory explains why this ancient practice creates such deep states of relaxation and bliss.
Detach from Thoughts
Often it's stressful thoughts of worry and fear that keep you in a constant state of 'fight or flight' which is the polar opposite of the relaxation response activated through the vagus nerve. Learning meditation techniques like mindfulness will help you disconnect from thoughts and give your nervous system a break and a chance to reset to a new normal where you can maintain a sense of ease. Through other techniques mentioned above like deep breathing and chanting you can also detach from thoughts and get similar results.
Written by Reese Jones
Get A FREE
Guided Meditation Series
with Chad Foreman